VNA vs PACS: Choosing the Right Medical Imaging Technology
Modern healthcare relies on medical imaging to deliver essential data that supports patient diagnosis and treatment planning and enables patient monitoring. Two acronyms at the center of this medical imaging technology are VNA vs PACS. Employed together in most situations, they represent two schools of thought about image management, each with profound ramifications for data access, workflow, & long-term planning.
This Dash Technologies blog will examine the fundamental distinctions between Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS) and Vendor Neutral Archives (VNA) to evaluate their advantages and challenges and explain the strategic necessity of transitioning between these systems for many organizations.
Understanding the Basics: VNA and PACS Defined
What is a Vendor Neutral Archive (VNA)?
A Vendor Neutral Archive (VNA) is a revolutionary medical imaging technology, which stores medical images & clinically related documents in a standard format with a standard interface. Standardization enables medical professionals to access images regardless of the proprietary equipment that created the images. VNAs collect, standardize, and store images from multiple PACS systems as a single, interoperable digital repository, without the need for siloed storage groups.
Key Features of Vendor Neutral Archive (VNA)
Vendor-neutral archives (VNA) are carefully designed for long-term, vendor-neutral storage of medical images, offering a centralized and interoperable solution. The following are the key features that drive VNA ahead in the medical imaging technology industry:
-
Vendor Neutrality
VNAs store medical images and documents in standard formats, such as DICOM, with standard interfaces provided, which makes the data available and manageable on any compatible platform, avoiding vendor lock-in. This enables easy integration in a wide range of imaging modalities & software vendors.
-
Centralized Storage and Consolidation
VNAs establish a unified repository for medical imaging and related clinical documents by merging data from various PACS and imaging systems into one easily accessible archive. Data management becomes more efficient while eliminating siloed storage repositories.
-
Standardization and Interoperability
Employing open standards such as DICOM for images and HL7 for other clinical information, VNAs facilitate seamless interoperability among various healthcare IT systems such as PACS, EHR (Electronic Health Record), and RIS (Radiology Information System). The system provides uninterrupted data transfer while establishing a long-term integration capability.
-
Scalability
VNAs are designed to handle the growing volume of imaging information, natively scaling to support the needs of large health systems and multi-facility networks.
-
Image Lifecycle Management (ILM)
VNAs enable organizations to automate image acquisition, storage, retention, and deletion according to clinical or regulatory needs through advanced data retention and lifecycle management systems.
-
Data Security and Privacy
VNAs incorporate strong security protocols, including encryption, access controls, and audit trails, to protect sensitive patient information and comply with healthcare regulations like HIPAA.
-
AI integration capabilities
VNAs now offer Gen-AI technologies for research and clinical use. This interface automates image analysis, annotation, and inference to improve diagnostics and processes.
VNA, PACS, or hybrid—get it right from the start.
Our healthcare IT experts deliver scalable, interoperable imaging solutions tailored to your workflow, security, and data accessibility goals. Work with a partner who understands both tech and care.
Book a ConsultationWhat is a Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS)?
A Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS) is a medical imaging technology that provides economical storage and convenient access to images from multiple modalities, such as X-ray, CT, MRI, and ultrasound. Electronic images and reports are digitally transmitted through the system, removing the need for manual filing and physical film jacket transportation. PACS systems traditionally depend on specific vendors and imaging systems, which restricts their ability to integrate with various technologies.
Key Features of Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS)
Picture Archiving and Communication Systems (PACS) automate medical image management by replacing outdated film-based methods with advanced digital alternatives. These essential features demonstrate why PACS stands as an indispensable asset for radiology departments:
-
Digital Image Storage and Retrieval
PACS serves as an electronic repository for medical images obtained from multiple imaging systems, including X-ray, CT scans, MRI scans, and ultrasound technology; enabling quick and secure retrieval for clinical use.
-
Integration with Imaging Modalities
PACS seamlessly connects to imaging equipment, allowing it to receive and store images automatically as soon as they are produced, ensuring a seamless workflow from image acquisition to diagnosis.
-
Image Viewing and Distribution
PACS includes advanced viewing workstations and tools for image manipulation, annotation, and analysis, supporting radiologists, clinicians in diagnosis and treatment planning.
-
Workflow Optimization
PACS augments clinical workflows with the capability of simultaneous image viewing by multiple users, remote consultation, and smooth integration into other health IT systems such as RIS and HIS.
-
DICOM Compliance
The PACS system stores and communicates images using the DICOM standard, which is compatible with most current imaging devices and software platforms.
-
Integration with Health Information Systems
PACS often communicates with Radiology Information Systems (RIS) and Hospital Information Systems (HIS) and integrates imaging data with patient information and clinical processes.
Key Differences: VNA vs PACS
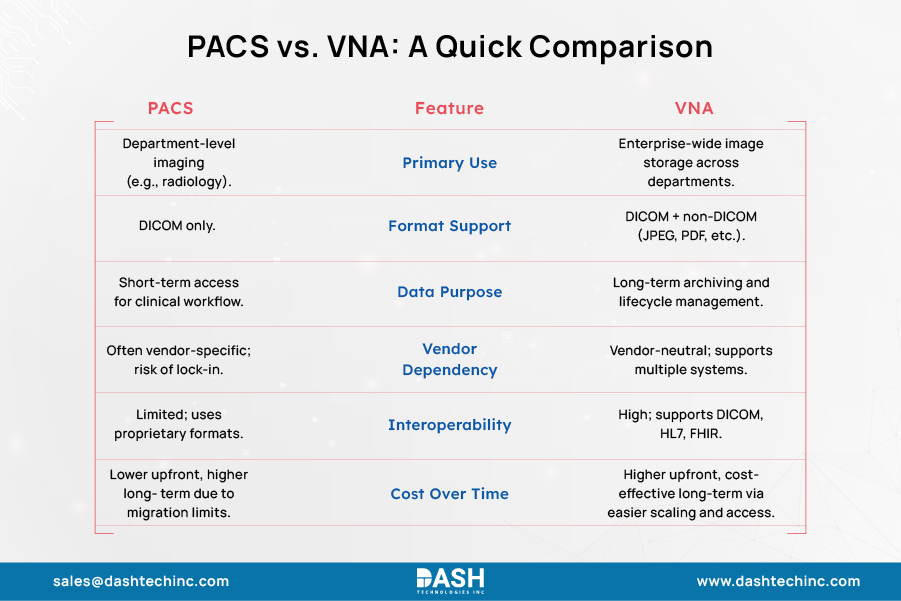
-
System Architecture and Focus
In the conversation of VNA vs PACS, the Picture Archiving and Communication System mainly interoperates with radiology modalities and its directly associated departments, with the goal of establishing seamless communication in its own domain. PACS excels at optimizing radiological imaging processes, receiving – storing images automatically, and communicating with Radiology Information Systems (RIS) and linking to Electronic Health Records (EHR).
>On the contrary, VNA has more extensive integration capabilities, designed to operate in a variety of departments and even in multiple healthcare organizations. It supports a wide range of formats apart from DICOM, including cardiology, pathology, dermatology, and a number of other specialties. -
Data Management Approach
Where PACS is focused on improving workflow with emphasis on immediate storage and retrieval for clinical use, VNA is geared towards long-term backup and archiving without vendor proprietary constraints. Essentially, VNA is designed for data migration (a “backend” system) while PACS facilitates data capturing, arranging, archiving, and sharing of medical image files (the “front-end”).
-
Vendor Relationship
PACS solutions usually require a particular vendor or imaging system which restricts their compatibility with various imaging technologies and complicates vendor switching. Such situations establish risks where long-term vendor lock-in becomes problematic.
VNAs are specifically designed to be vendor-neutral, supporting multiple formats from various vendors and eliminating dependency on any single provider. This promotes flexibility and makes it easier to adapt to changing technological needs. -
Interoperability and Standardization
The majority of PACS solutions adhere to the DICOM standard for image storage as well as transfer but tend to utilize proprietary tags or vendor-specific protocols. This practice causes the problem of compatibility when attempting to integrate with other systems or transfer data to another PACS, eventually causing vendor lock-in.
VNA is architected for actual interoperability. Images and metadata are stored in standard formats (DICOM, HL7, FHIR), with no proprietary tags, allowing compatibility across multiple vendors and systems. Standardization allows for seamless data sharing and future-proofing the organization’s imaging infrastructure. -
Cost and Implementation Considerations
PACS is cheaper for single-department or small-scale installations but, owing to proprietary constraints, becomes costly when growth, upgrades, or migrations are involved.
>VNA has a higher initial cost, especially integration with current systems; however, it has long-term advantages, including without vendor lock-in, simplified data migration, and consolidated storage management.
When to Choose VNA vs PACS
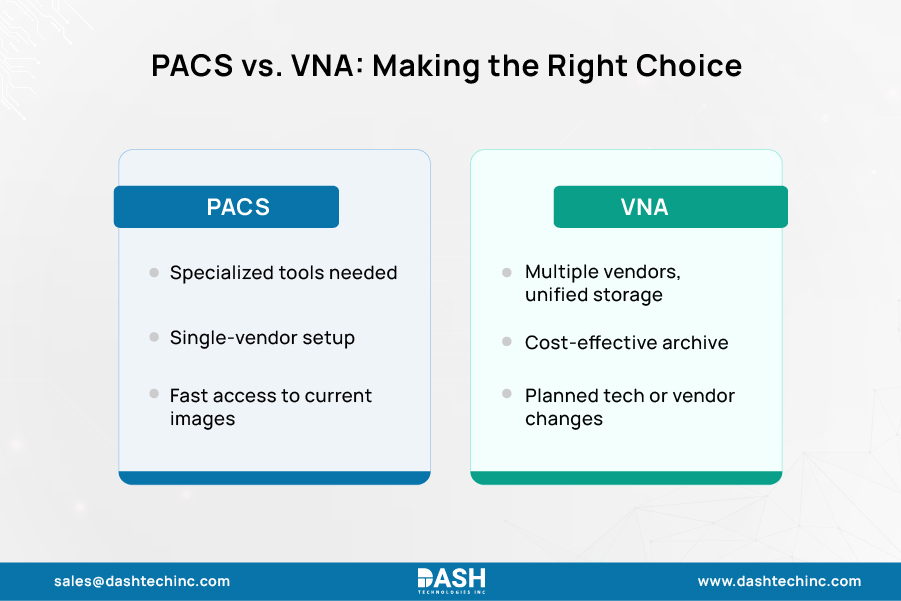
Choose PACS When:
- Settings where specialized viewing and manipulation tools are prioritized.
- You employ solutions from one provider only, allowing for easy integration.
- Your operations need immediate access to routinely utilized images.
Choose VNA When:
- Your equipment comes from different vendors, and you require a consolidated storage platform.
- You must store historical images cost-effectively.
- You anticipate vendor changes or technological advancements.
- Your organization demands a unified storage solution between departments such as radiology and cardiology.
Explore Our Guide on Medical Imaging Software Development: Step-by-Step Process
Looking to Modernize Your Medical Imaging Workflows?
We help healthcare organizations implement scalable, secure, and interoperable solutions tailored to their unique imaging needs—whether you’re transitioning from legacy PACS to VNA, integrating systems across departments, or improving data access for clinical teams.
Partner with us to schedule a consultation and discover how Dash Technologies can future-proof your imaging infrastructure and enhance care delivery.
About Dash

Dash Technologies Inc.
We’re technology experts with a passion for bringing concepts to life. By leveraging a unique, consultative process and an agile development approach, we translate business challenges into technology solutions Get in touch.