Embedded Software vs. Cloud in MedTech: A Guide for Innovation
In the heart of modern healthcare, a technological revolution is unfolding, powered by two dynamic forces: embedded software and cloud platforms. These innovations are transforming the way medical devices operate and how we manage patient data.
With the healthcare cloud computing market expected to hit around $120.6 billion by 2029 and the market for connected medical devices growing over 19.6% each year towards $273.6 billion by 2030, it’s super important for decision-makers to grasp what each option means.
The implications for patients and providers are high stakes in healthcare, where the choice of technology determines the safety of a patient’s life, regulatory compliance, and the outcomes of their care.
Understanding Embedded Software in Medical Devices
Embedded software development is the basis for today’s medical devices providing the intelligence for a wide spectrum of simple glucose meters to sophisticated surgical robots. These specialized programs are custom-made for the medical market and have to withstand rigorous testing to ensure compliance with safety regulations as well as the guidelines laid down by the International Medical Device Regulators Forum.
Unlike general-purpose software, embedded software in medical devices is usually written specifically for the medical industry and implemented into hardware. These programs must be extremely accurate and reliable, enabling medical devices to perform their functions without error.
Reliability is another important quality of an embedded system, as they are required to operate reliably without failure. Most medical devices that use embedded software have fault-tolerance techniques, redundant mechanisms, and fail-safe features to ensure that the system will work even if individual components fail. These devices are designed to comply with industry standards such as IEC 62304 for software development, ISO 14971 for risk management, & IEC 62366 for usability engineering.
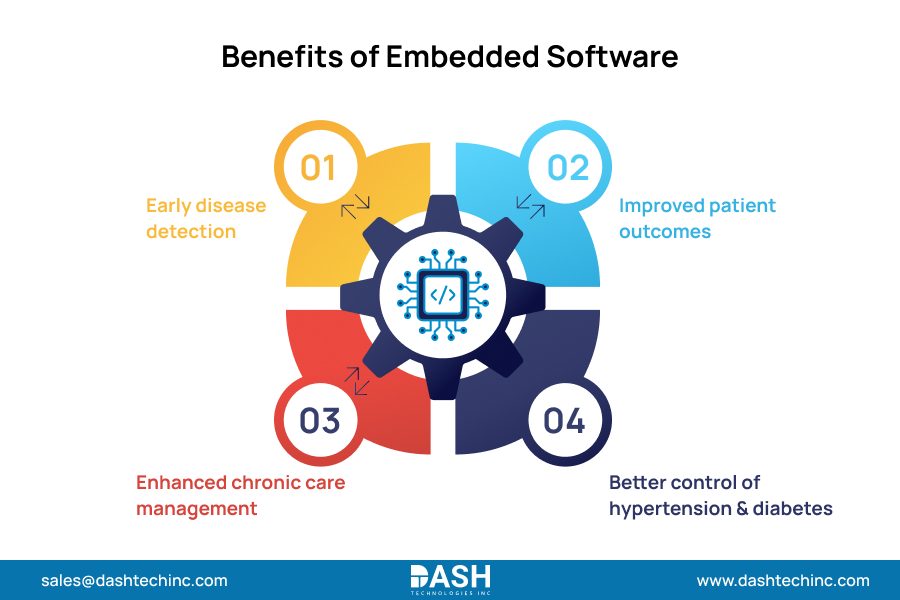
Enhanced monitoring ability is one of the primary benefits of embedded systems in medical devices. The systems enabled the creation of wearable devices that continuously monitor various biometric data. This has helped in:
- Faster detection of diseases
- Better patient outcomes
- Improved care for chronic conditions
- Better management of hypertension and diabetes
Cloud Platforms in Healthcare Technology
Cloud-based healthcare solutions represent a shift toward distributed computing architectures that use remote servers, flexible infrastructure, and internet access to deliver healthcare services & store health information. This is a revolutionary method of changing the means through which healthcare organizations store, process, and analyze information, from device-centric to service-centric.
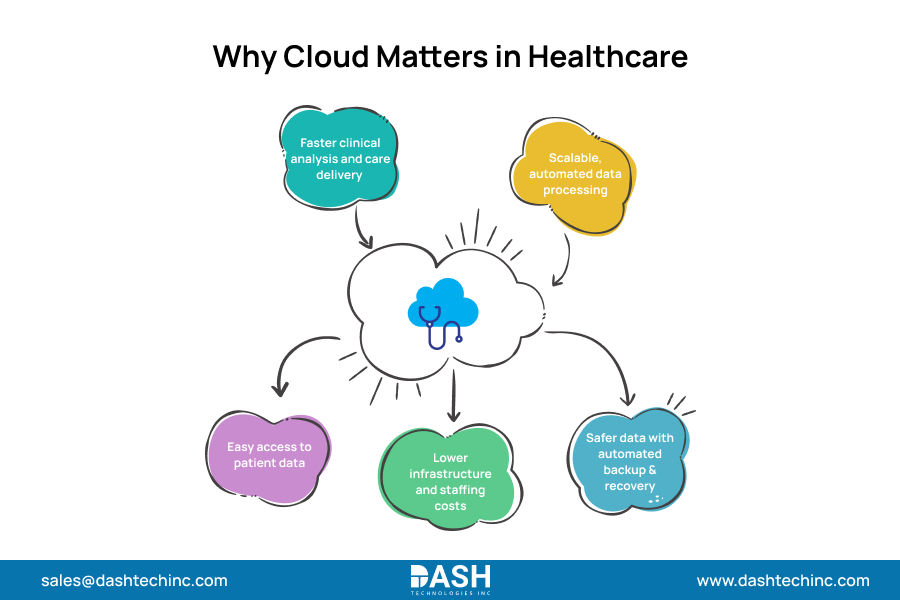
The benefits of cloud computing in healthcare are multifaceted:
- Accelerated clinical analyses and care processes
- Automated data processing and scalability
- Increased patient data accessibility
- Significant reduction in network equipment and staff costs
- Reduced risk of data loss through automated backup and disaster recovery protocols
Telemedicine and remote care are the key factors that prompt the use of cloud computing in healthcare. Cloud computing enables the creation and implementation of telemedicine platforms that facilitate secure video consultations, real-time health monitoring, and seamless data sharing between doctors and patients, regardless of their geographical location.
The advanced cloud analytics and artificial intelligence capabilities enable the medical industry to utilize these technologies for more accurate diagnoses, disease prediction, and customized treatment plans. Cloud computing acts as the foundation for data-driven decisions in the healthcare sector.
Cloud Tech for MedTech Growth
Leverage our end-to-end cloud expertise to modernize your infrastructure, improve data accessibility, and drive real-time decision-making — all while staying compliant and future-ready.
Partner with UsComparative Analysis: Embedded vs. Cloud Approaches
The choice between embedded software and cloud platforms for MedTech involves trade-offs along multiple dimensions that significantly impact patient care, efficiency, and competitive positioning. Understanding the characteristics of these differences includes looking at performance, costs, security, and scalability.
Performance and Reliability
Embedded systems excel at real-time performance and reliability and can operate independently of network connectivity. LVGL, for example, is designed to display graphical components in real-time without compromising responsiveness and is ideally suited to time-critical medical uses where slowdowns would compromise patient safety.
Cloud-based systems, although offering greater processing capability for sophisticated analysis, are dependent on network connectivity and are prone to the risk of latency, which can be disastrous for life-critical care applications.
Resource Utilization and Costs
Embedded software is optimized for low resource consumption. Therefore, it is suitable for battery-powered devices and for those with low power consumption. For example, a portable medical device, such as an ECG monitor or a handheld ultrasound, is low-power and requires reliable performance. Cloud solutions, conversely, are cost-effective, as they reduce the expenses of hardware and in-house maintenance. Cost-effectiveness is achieved through the infrastructure-as-a-service and software-as-a-service models.
Scalability and Flexibility
The cloud offers a far higher level of scalability than an embedded system. It is also possible to scale through a cloud platform as Electronic Health Records and other applications continue to grow at a rapid pace. For a healthcare system that is undergoing rapid growth, automated scalability is a huge plus. Embedded systems offer less scalability but are more customized and optimized for specific medical devices.
Security and Compliance
Both options have stringent regulatory requirements, but they take on different security models. Embedded systems can have isolated security solutions, but they are susceptible to physical tampering. Cloud platforms, such as BioT, offer medical-grade security and compliance from the get-go with FDA, MDR, HIPAA, GDPR, SOC2, and HITRUST compliance. On the other hand, cloud solutions rely on third-party security solutions and may be more prone to data breaches.
IoT in Healthcare: Bridging Embedded and Cloud Technologies
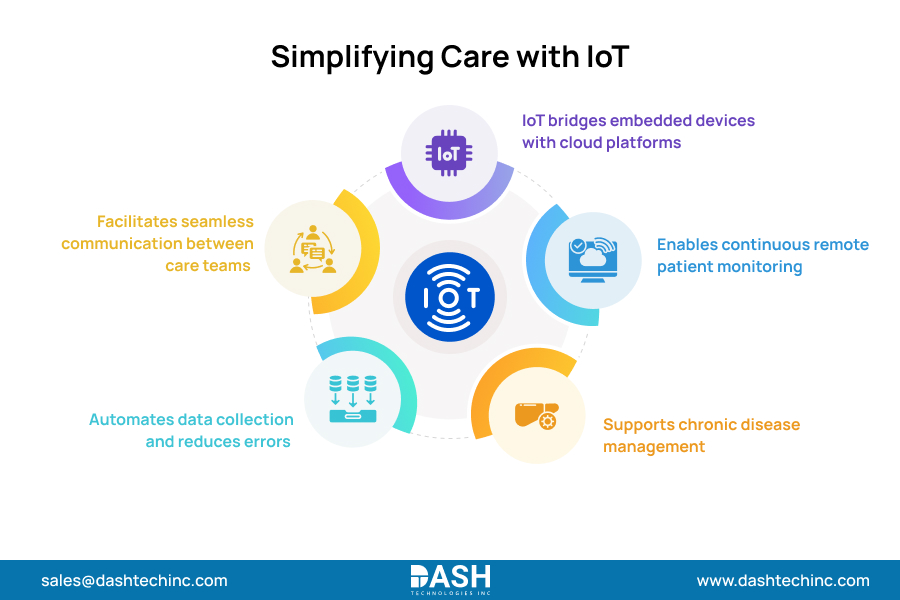
The Internet of Things in Healthcare, also called the Internet of Medical Things (IoMT), brings together embedded systems and cloud platforms to form integrated ecosystems that facilitate better patient care delivery. The Internet of Things comprises physical devices equipped with sensors, software, and communication devices that collect, transmit, and process data without human involvement.
Today, connected medical devices are changing the practice of patient monitoring by making it possible to monitor patients’ vital signs and symptoms in real-time, and that too, remotely. Monitoring patients’ heart rate, oxygen saturation, and blood pressure remotely can enable early detection of irregularities before the situation can develop into a health issue. This is especially true for chronic conditions where continuous monitoring is critical for the best patient outcomes.
IoT technology facilitates a greater connection between patients, doctors, and healthcare teams. Patients can be more involved in managing their own care, and doctors can monitor their health with greater accuracy. This extends to in-home care settings, where patients with chronic illnesses can monitor vital signs, fall detection, track medication, and even initiate telemedicine appointments through home IoT hubs and wearable devices.
IoT through connected medical devices helps streamline clinical workflows by automating data entry, reducing the time required for manual entries, decreasing administrative tasks, and minimizing human errors. It makes the delivery of healthcare more efficient and increases accuracy at every step of the care process.
Final Thoughts
The choice between embedded and Cloud-based healthcare solutions, or the use of both in tandem, is a critical decision for MedTech innovators. While embedded systems remain critical for real-time, safety-critical functionality at the device level, cloud platforms offer unparalleled scalability, data insights, and remote capabilities.
With a careful combination of the two, they enable new advancements, such as IoT in Healthcare and connected medical devices, to become a reality. MedTech providers can improve patient outcomes and reduce costs. As AI, edge computing, and other factors continue to transform the future, providers need to adopt both to deliver cost-effective, patient-centric solutions. Partner with Dash Technologies to get best-in-class embedded software development and cloud-based healthcare solutions to fit your needs and help you stay compliant every step of the way.
About Dash

Dash Technologies Inc.
We’re technology experts with a passion for bringing concepts to life. By leveraging a unique, consultative process and an agile development approach, we translate business challenges into technology solutions Get in touch.