AI and Predictive Analytics in Healthcare: Ethical Challenges, Regulation Framework, and Future
Predictive analytics in healthcare enable providers to detect health threats sooner. Thus, providers can make evidence-based decisions on time. It uses patient data from EHRs, diagnoses, and daily activities. This helps spot risks early and supports quick clinical decisions using AI models. It automates hospital operations to improve diagnostics and manages more data for patient care.
AI helps with automation and improves decision-making. The correctness of AI software depends on the data and systems they work on. This also impacts other areas such as the use of medical devices, real-time monitoring tools, and telemedicine platforms that rely on accurate predictions for remote diagnosis and patient management.
MedTech companies and healthcare administrators also rely on predictive models to streamline device usage, patient throughput, and compliance with care quality metrics.
Let’s explore what are the key use cases, ethical challenges faced, and strategies to overcome these challenges when healthcare systems and MedTech companies want to integrate AI and predictive analytics.
How is AI Used in Healthcare?
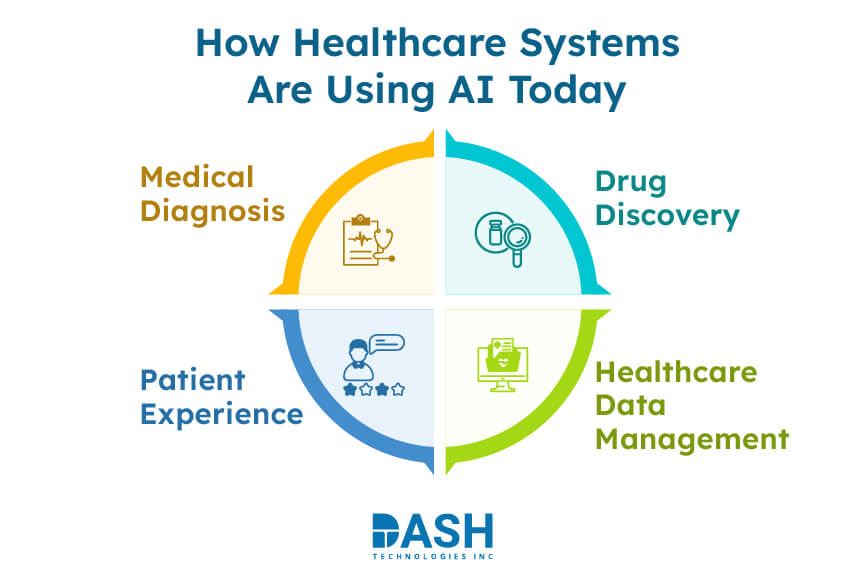
There’s no wonder how AI has been transforming every industry and sector, majorly impacting healthcare ecosystem. From automating routine clinical responsibilities to detecting the early signs of patients’ diseases – that’s how far has AI in healthcare evolved. To understand it better, let’s talk about a few areas and its AI implementation.
-
Medical Diagnosis
Diagnostic error has the potential to cause harm to patients and incur unnecessary expense. Medical images, laboratory data, and patient history are analyzed by AI. It helps diagnose diseases with greater speed and accuracy. This minimizes misdiagnoses and enables physicians to make improved decisions. AI spots pattern that people might overlook due to time limits or lack of information.
-
Drug Discovery
AI speeds up drug discovery by finding strong compounds. It also predicts side effects and chooses the right candidates for the clinical trial. AI helps researchers by analyzing large data sets. This lets them find the best drug candidates. As a result, they save both time and money in drug development.
-
Patient Experience
AI enhances patient engagement by performing tasks like scheduling appointments, sending reminders to patients a, and following up on care instructions automatically. AI diagnoses are quicker and more accurate, leading to tailored care plans. Such efficiencies allow providers to see more patients without compromising quality.
Telemedicine providers use AI to improve virtual consultations and deliver consistent patient education, which helps improve satisfaction and follow-up compliance across geographies. -
Healthcare Data Management
Healthcare systems manage a lot of information including patient records, diagnostic imaging, clinical notes, and operational data. Organization and management of this information may become too much to handle without sophisticated data systems or automation.
AI helps insurance companies assess claim risks, detect fraud, and improve reimbursement strategies using predictive models.
MedTech firms and medical equipment manufacturers apply predictive analytics for product development, equipment monitoring, and regulatory compliance—ensuring efficiency and patient safety across the system.
Accelerate MedTech Product Development with AI and Predictive Intelligence.
Leverage data, automation, and real-time insights to streamline workflows, reduce time-to-market, and build smarter, compliant healthcare solutions.
Let’s Build Smarter Systems Together!Predictive Analytics for Value-Based Patient Care
Predictive analytics in healthcare makes future predictions using historical as well as ongoing data. It analyses EHRs, imaging, lab reports, and patient activity to find patterns that show possible health risks before it’s too late.
One major benefit is the early detection of diseases. Predictive models can spot patients at risk based on their historical data. They help flag early warning signs for any chronic diseases, face readmission, or suffer complications like sepsis. Healthcare teams can step in sooner with preventive measures.
With predictive analytics in hospital operations, staff and resource allocation can be done more efficiently. For example, it can predict ICU bed needs and forecast staff requirements during peak illness seasons.
At the level of individual patients, predictive analytics allows for more personalized care plans, considering patient’s risk profile. This assists physicians in suggesting lifestyle modifications, titrating medications, or following up based on anticipated results, improving patient outcomes. It supports a shift toward value-based care. This helps healthcare systems prepare rather than respond, boosting efficiency and safety at all levels.
Health insurance providers and financing bodies use predictive analytics to identify and understand patient groups with high expected healthcare costs, also manage population health more effectively.
Hospitals leverage it to forecast equipment utilization, bed turnover, and elective surgery backlogs, which enhances care delivery and supports MedTech device readiness. In medical tourism, predictive models help anticipate demand, design specialized treatment packages, and streamline cross-border care coordination.
Ethical Challenges in AI and Predictive Analytics
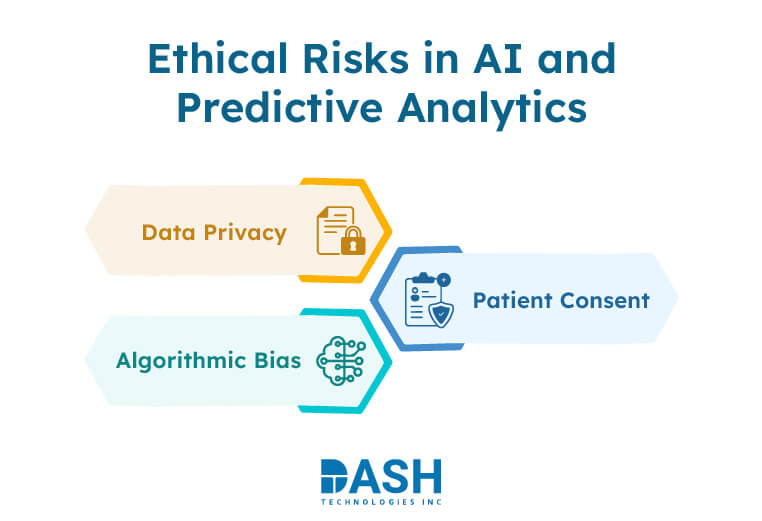
As AI and predictive analytics become more common in healthcare, ethical concerns are critical. Areas like data privacy, bias, and patient consent must be addressed to support safe and fair adoption.
- Data Privacy
AI systems and predictive analytics use vast quantities of patient data to work at high efficiency. They include EHRs, imaging data, and real-time monitoring data. Protecting this information is paramount. Healthcare individuals are supposed to adopt a high level of data encryption, good access control, and maintain records in accordance with the regulations like HIPAA. - Algorithmic Bias
Predictive models that use biased or incomplete data can create unequal risk assessments. This issue affects both AI systems and analytics tools. Regular retraining with inclusive datasets is required. - Patient Consent
Patients need to know their options when doctors use AI and predictive analytics for treatment plans or diagnoses. They must understand how the system operates, what information it utilizes, and its limitations. Clear consent processes help engage patients in decision-making. This involvement plays a vital role in better patient outcomes.
How Can Healthcare Systems Ensure Ethical Use of AI and Predictive Analytics?
AI and predictive analytics are bestowed with a voice to offer transparency, justice, and fair application. The key issues include:
- Data Governance
There must be a solid data governance structure that includes anonymizing data, setting access controls, and complying with data protection laws. This builds patient trust and enables AI systems and predictive algorithms to function safely and responsibly. Robust governance also ensures compliance with international data-sharing standards in areas like hospital equipment, health insurance underwriting, and remote monitoring devices. - Bias Detection
To avoid bias in predictions, AI systems must be trained using diverse and representative datasets. Techniques like reweighting, sampling correction, and stratified data partitioning help improve data balance before model training.
Models such as adversarial debiasing, fairness-aware algorithms (e.g., Fairlearn), and counterfactual fairness frameworks can be used to detect and correct bias during development.
Post-training, regular evaluation using tools like AIF360 and fairness metrics such as equalized odds or demographic parity help maintain fairness across patient groups. These methods support consistent and reliable healthcare predictions over time. - Explainable AI & Trust-building
Explainable AI helps doctors see how systems make decisions. When clinicians grasp AI outputs, they can confirm results and improve patient discussions. Generative AI supports healthcare by summarizing clinical information or simulating care scenarios.
Transparency between providers and patients builds trust, and clear explanations boost this trust. This understanding leads to better patient outcomes and safer AI use in care delivery.
Regulation Framework for AI and Predictive Analytics
There are various standards and guidelines that govern the ethical and responsible application of AI and predictive analytics. These guarantee patient safety, data privacy, and clinical effectiveness throughout systems.
- Global Standards
The World Health Organization (WHO) has developed standards for artificial intelligence and predictive analytics. It focuses on equity, transparency, and accountability to promote cooperation, making sure that tools such as those used for diagnostic imaging are safe and effective. - National Guidelines
The American Medical Association (AMA) focuses on ethics, clinical data, and fairness. This framework aids healthcare professionals in assessing AI applications and predictive modeling. The goal is to ensure that these tools are safe and effective for patient care. - SHIFT Framework
The SHIFT framework identifies principal principles: sustainable, human-centric, inclusive, fair, and transparent. The framework helps align AI-powered diagnostics or predictive risk models with changing clinical needs. It also promotes responsible and ethical deployment. - RESTART Framework
The RESTART framework uses blockchain to enhance transparency and ensure secure, auditable data systems. This is essential for predictive analytics models and various types of artificial intelligence in healthcare, especially in critical areas like medical data management and diagnostics.
Navigating the Future of Healthcare Intelligence
The future of healthcare is changing through digital system evolution. With increasing use of artificial intelligence in the clinical environment, the attention is not only on what it can do, but how it needs to be responsibly used.
The foundation is how machines process and learn from clinical data. The types of artificial intelligence in healthcare include machine learning, deep learning, and natural language processing. Healthcare professionals use these to review lab results, find patterns in medical scans, and cut down manual data entry.
The next step in this transformation is value-based care. Predictive analytics in healthcare uses patient history and behaviour patterns to identify risks earlier. This supports timely decisions, especially in managing chronic conditions.
Emerging technologies like generative AI in healthcare are also being explored for tasks such as summarizing clinical notes or simulating health outcomes. These applications need clear rules, validation, and collaboration between healthcare and technology teams.
As predictive technologies scale, their role in global health insurance models, international clinical trials, and regulated telemedicine ecosystems will require more scrutiny and cooperation.
Progress in this space depends on practical planning, data governance, and strong collaboration to ensure AI and predictive tools meet real clinical needs.
Conclusion
AI is revolutionizing healthcare systems, assisting in diagnostics, choice of treatments, and resource allocation. However, its application poses ethical problems that must be solved. Clear data policies and regular bias checks enable effective use of AI. This will support clinical goals and preserve patient trust. AI can be used in care by focusing on patient needs, fairness, and accountability. Using predictive analytics in healthcare allows for early risk detection and better planning. This strengthens care outcomes throughout the system.
Integrating AI across diverse healthcare such as medical devices, insurance models, telemedicine services, and clinical research ensures that innovation stays aligned with ethical, scalable care delivery.
For tailored AI solutions in healthcare, contact our DASH team helps you implement ethical, efficient, and scalable systems to improve care outcomes.
About Dash

Dash Technologies Inc.
We’re technology experts with a passion for bringing concepts to life. By leveraging a unique, consultative process and an agile development approach, we translate business challenges into technology solutions Get in touch.